Connecticut Sea Grant launches website to help coastal homeowners
The website serves as a decision support tool. Connecticut Sea Grant announces a new website intended to assist coastal Connecticut beach property owners and beach
Scroll down to view posts

The website serves as a decision support tool. Connecticut Sea Grant announces a new website intended to assist coastal Connecticut beach property owners and beach

The Dune It Right manual explains dune ecology. This tool is for anyone undertaking a dune restoration or rehabilitation project. It explains what species uses what parts of the beach, how to avoid damaging habitat and how to avoid creating a monoculture.

Scientists in Maryland have published numerous studies on the impacts of climate change on the Mid-Atlantic region, but communicating the results of that research has proved difficult. Many residents in the state’s coastal communities lack a good understanding of the risks that climate change and sea level rise in particular pose to their way of life. In 2012, Maryland Sea Grant held a statewide climate change forum to inform efforts to share and discuss the findings of climate science with these communities.

Maryland Sea Grant supported a research project to develop a Nutrient Loading Model for the Delmarva Peninsula. Other collaborators and funders on the effort included Sea Grant programs in Delaware and Virginia.
New York Sea Grant’s Great Lakes Coastal Processes and Erosion homepage provides information focused on the educational needs of New York’s Great Lake’s shoreline property owners, resource users and decision makers, marine contractors, and recreational boaters.

This website contains information, data, and tools that individuals, communities, and governments at all levels can use to develop, inform, and enhance their sustainable working waterfront initiatives.

The Governors’ South Atlantic Alliance (GSAA) Data Portal is an online toolkit and resource center that consolidates available state, regional, and federal datasets into one location for Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, and North Carolina. This allows users of the Portal to learn about the region’s data resources, explore a robust repository, and visualize these data via the Portal tools. Developed by the Southeast Coastal Ocean Observing Regional Association (SECOORA) with NOAA support through the S.C. Sea Grant Consortium, the GSAA Portal provides a foundation for long-term collaborative planning in the South Atlantic region for a wide range of coastal uses.

Many residents of South Carolina and beyond aspire to live at the beachfront. To better prepare people seeking beachfront homes (as well as those already enjoying life at the beachfront) regarding specific hazards and regulations, the S.C. Department of Health and Environmental Control Office of Ocean and Coastal Resource Management, with significant contributions from the S.C. Sea Grant Consortium, has produced the South Carolina Guide to Beachfront Property. Included is information on typical hazards homeowners are likely to face (hurricanes, erosion, flooding, wind, and earthquakes), insurance information, and important state regulations regarding construction and renovation practices.

With the vast majority of land-use decisions made at the local level, community officials are instrumental in influencing and directing development and conservation efforts. The S.C. Coastal Communities Initiative is a collaborative land-use planning and water quality small grants program for local decision-makers. The purpose of the Initiative is to assist coastal communities with the development and implementation of land management policies and practices to reduce polluted stormwater runoff, protect local natural resources, and encourage sustainable development. Coastal communities participating in the Initiative are eligible to receive grants ranging from $2500 to $5000 to address a variety of issues related to open space preservation, natural resource-based planning, water quality management, alternative transportation, sustainable community planning and design, and zoning ordinances and regulations.

The Santa Barbara Area Coastal Ecosystem Vulnerability Assessment for Local Communities (SBA CEVALC) is aimed at assisting the Cities of Santa Barbara, Carpinteria, and Goleta and the County of Santa Barbara in planning for adaptation to climate change. Three of the state's leading ecological and climatological research programs including: the UCSB Coastal Long-Term Ecological Research Project, the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and USGS, are accomplishing the project in close collaboration with the three cities and County. Community input is integral to the project with staff from relevant city/county departments participating through workshops and review.

King Tides, or extreme high tides, offer the chance to view what the future might look like with higher sea levels. The King Tides Project directs citizens to capture images of King Tide events and upload them onto the website. The Washington King Tides project is part of an international collaboration.
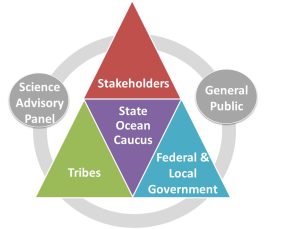
As a member of the State Ocean Caucus, Washington Sea Grant is a member of the State planning team charged by the State legislature to develop a marine spatial plan off Washington’s outer coast. The plan will provide better baseline information, ecosystem indicators, analyses to support coastal management decision-making, recommendations for siting new uses, implementation framework across agencies and sectors, integration of other existing policies and management and an adaptive management strategy. Washington Sea Grant plays a central role in this process by leading outreach, coordinating scientific review of data and projects, developing indicators of human well-being and economic health of the coast.

This report is a regional social science collaboration highlighting the gaps in knowledge related to people and marine environments. Robust social science is a fundamental aspect of ecosystem-based management; and moreover, provides necessary information for understanding resilience and vulnerability to human populations.
North Carolina Sea Grant extension partners with the N.C. Department of Insurance and the Institute for Businesses and Home Safety Fortified training program to increase building and design standards, including workshops to train builders, as well as training for building code inspectors and other professionals.

The cultural dimensions of coastal ecosystems framework and guidelines for best practices is a conceptual tool to guide scientists, managers and community practitioners in their efforts to: (1) identify potential cultural impacts in impacted areas; (2) select and develop methods for working with communities to characterize their cultural impacts. Cultural aspects are often ambiguous and moreover absent from vulnerability and resilience assessments and this guidelines offers clear and specific identification of cultural aspects that have been or could be impacted in events.

In collaboration with Washington Land Grant partners, Washington Sea Grant provides training, resources and opportunities to volunteers interested in learning about freshwater environments and the watershed and marine systems to which they are tied. The volunteers then contribute to improving their communities through monitoring, enhancement, restoration and outreach.

Virginia Sea Grant has a legal program now and they have been focusing on resiliency issues—conducting legal and policy research for local community clients on issues such as flood insurance, community rating systems, potential disclosure issues, potential local community liability risk associated with not taking adaptation steps. They have also provided analysis to the Governor’s Climate Commission that is currently underway and the General Assembly’s Secure Commonwealth Panel that finished up work last month.

This document is intended as a guide for entities interested in assessing their vulnerability to coastal hazards. Coastal vulnerability is a complex topic that requires an understanding of some basic terms, concepts, and historical context to be effectively assessed.

Coastal communities across the nation are faced with the challenge of how to adapt to coastal inundation associated with climate change and sea level rise. As part of the National Sea Grant Coastal Communities Climate Adaptation Initiative (CCCAI), the New Jersey Sea Grant Consortium (NJSGC) and its partners, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Office of Coastal Management (NJOCM), Monmouth University Urban Coast Institute (UCI) and Stevens Institute of Technology, conducted community-based, climate adaptation demonstration projects in Cape May Point, Little Silver and Oceanport, New Jersey.

This report from a year-long study from Sea Grant and the NOAA North Atlantic Regional Team (NART) identifies some best practices that communities can use locally for adapting to climate change. “Cost-Efficient Climate Change Adaptation in the North Atlantic” is a compilation of best practices shared by 34 towns and cities (ME to VA) willing to share the steps that they have taken towards successful adaptation. The report also contains an interactive map.

Maine Sea Grant has organized a number of tours, during which Southern Maine coastal property owners, local officials, and community members visit coastal properties in Saco, Wells, and Ogunquit where action has been or could be taken to make them more resilient to flooding, erosion, and extreme storm events.

This online Guide was created by Maine Sea Grant to help coastal property owners and municipal officials identify features and different types of hazards on the Maine coast, and evaluate potential responses and actions. This guide is an outcome of the project, Coastal Community Resilience: Developing and Testing a Model of State-based Outreach.
An integrated assessment research project and deliverables to support Clinton River watershed decision-makers in water resources management.

The Great Lakes Beach, Tributary, and Nearshore Water Quality: Hydrologic and Hydrodynamic Data and Model Assimilation website hosts a water quality forecasting system for use at targeted beaches throughout the Great Lakes.
North Carolina Sea Grant and the N.C. Coastal Resources Law, Planning and Policy Center cover a variety of topics related to resiliency.

North Carolina Sea Grant funded research to determine impacts of rerouting water into the Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge as part of a proposed wetland restoration project.

This guide focuses on basic question to consider as an investor in coastal real estate, emphasizing the importance of having an understanding of the potential risks and consequences of living on the ocean’s edge.

The purpose of the 242 page guidebook is as a resource to reduce the risk to coastal development by planning for natural hazards such as erosion, flooding, tsunami, and hurricanes. The guidebook uses scientific and technically-based standards for hazard mitigation and provides recommendations for implementation (e.g., guidance, industry standards, policy and the use of existing regulations) that minimize burden to the regulated community.

In light of projected sea level rise and adaptation responses (i.e., accommodate, protect, and retreat), this paper examines the interactions among climate change, the regulation of shoreline development in Hawai‘i, and Constitutional law regarding unpermitted takings of private property for public benefit.
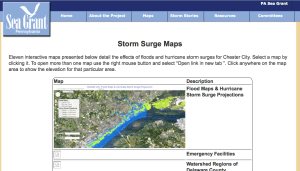
The Chester Climate Adaptation Team produced this series of 11 interactive Google Maps to assess the risk to the City's population, infrastructure, and environment from varying levels of flooding.

New Hampshire Sea Grant helped identify community adaptation strategies for the partner members of the Coastal Adaptation Workgroup (CAW), including a matrix of over 40 actions that communities can take to improve their climate adaptation capacity and implementation.
These are participatory mapping tools that a number of Sea Grant programs are using for community-based work addressing both climate and stormwater issues.
The StormSmart Coast website serves as a “resource for coastal decision makers looking for the latest and best information on how to protect their communities from weather and climate hazards” (http://stormsmartcoasts.org/)
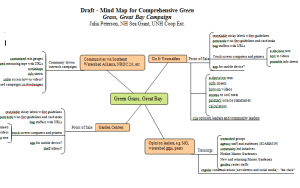
This tool was used to illustrate how social science findings could be used in a watershed wide non-point source pollution reduction campaign.

These tools are the result of a multi-state, integrated Sea Grant /Cooperative Extension coordinated project that supported both turf and social science research to reduce nitrogen losses from turf care and maintenance by do-it-yourself'ers.

Connecticut Sea Grant and CLEAR developed a web-based tool which leads resource managers through the process of developing a long-term habitat based management plan with information provided on coastal habitat types, management and restoration so as to maximize the long term resilience of natural areas.