Coastal Climate Adaptation Initiative
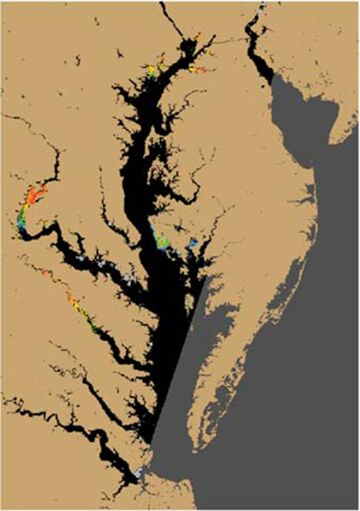
Woods Hole Sea Grant funded a climate adaptation project designed to provide regional and local predictions of future coastal storm activity and sea-level rise to user groups within the region and to promote wise utilization and conservation of resources.
Coastal Climate Adaptation Initiative Read More>